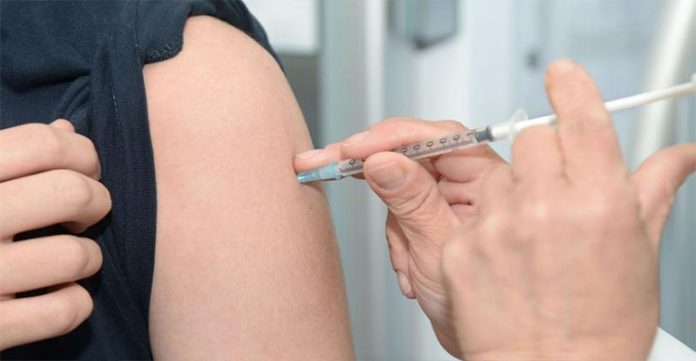
In the latest study, a cocktail of Covid 19 vaccines seems to be proving better than the usual two doses. Study recently showed that people who received their first vaccine dose of the Oxford-AstraZeneca Covid 19 vaccine and received mRNA shot for their second dose faced a lower risk of infection.
Study Conducted Over 700,000 Individuals
The study has been published in the journal, The Lancet Regional Health – Europe. It points out the higher effectiveness of the Covid 19 vaccines in a mix-match situation. A team from the Umea University, Sweden conducted a study of 700,000 individuals.
ALSO READ: One Covid 19 Vaccine Can Nearly Protect Against Similiar Covid 19 Infection; Research
Out of these, 67 percent showed lower risk infection for people who had received a combination of Oxford-AstraZeneca plus Pfizer-BioNTech. And around 79 percent showed lowered risk with the oxford/AstraZeneca and Moderna. Both were compared to the people who haven’t received any dose of vaccinations at all.
Oxford-AstraZeneca Doses Ensure 50 Percent Risk Reduction
However, for the people who have received around two doses of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine, the risk reduction was at 50 percent. These risk estimates were observed after accounting for differences regarding date of vaccination, age of the participants, socioeconomic status, and other risk factors for Covid-19.
Peter Nordstorm, Professor of geriatric medicine at Umea University said that receiving the vaccines that are approved is better than not receiving any vaccines at all. He said that their studies have shown that people who have received an mRNA vaccine after the first dose of a vector-based vaccine have a greater risk reduction.
ALSO READ: “Scientific Nonsense” Says Russia; British Security Forces Accuse Of Stealing Covid Vaccine Recipe
The estimates of the effectiveness apply to the Delta variant which was seen during the follow up period.
Prior researches have showed that the mix and match vaccine generated a strong immune response. However, it was unclear to the extent of which the schedules may reduce the risk of infection.